My IoT deCodeD Sample Temperature Code Page
Sample Temperature Code Page
TEMPERATURE OUTPUT TO SSH TERMINAL
This is a basic Python program that will output the temperature readings in Fahrenheit and Celsius to your SSH terminal:
import os
import glob
import time
os.system('modprobe w1-gpio')
os.system('modprobe w1-therm')
base_dir = '/sys/bus/w1/devices/'
device_folder = glob.glob(base_dir + '28*')[0]
device_file = device_folder + '/w1_slave'
def read_temp_raw():
f = open(device_file, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
return lines
def read_temp():
lines = read_temp_raw()
while lines[0].strip()[-3:] != 'YES':
time.sleep(0.2)
lines = read_temp_raw()
equals_pos = lines[1].find('t=')
if equals_pos != -1:
temp_string = lines[1][equals_pos+2:]
temp_c = float(temp_string) / 1000.0
temp_f = temp_c * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32.0
return temp_c, temp_f
while True:
print(read_temp())
time.sleep(1)
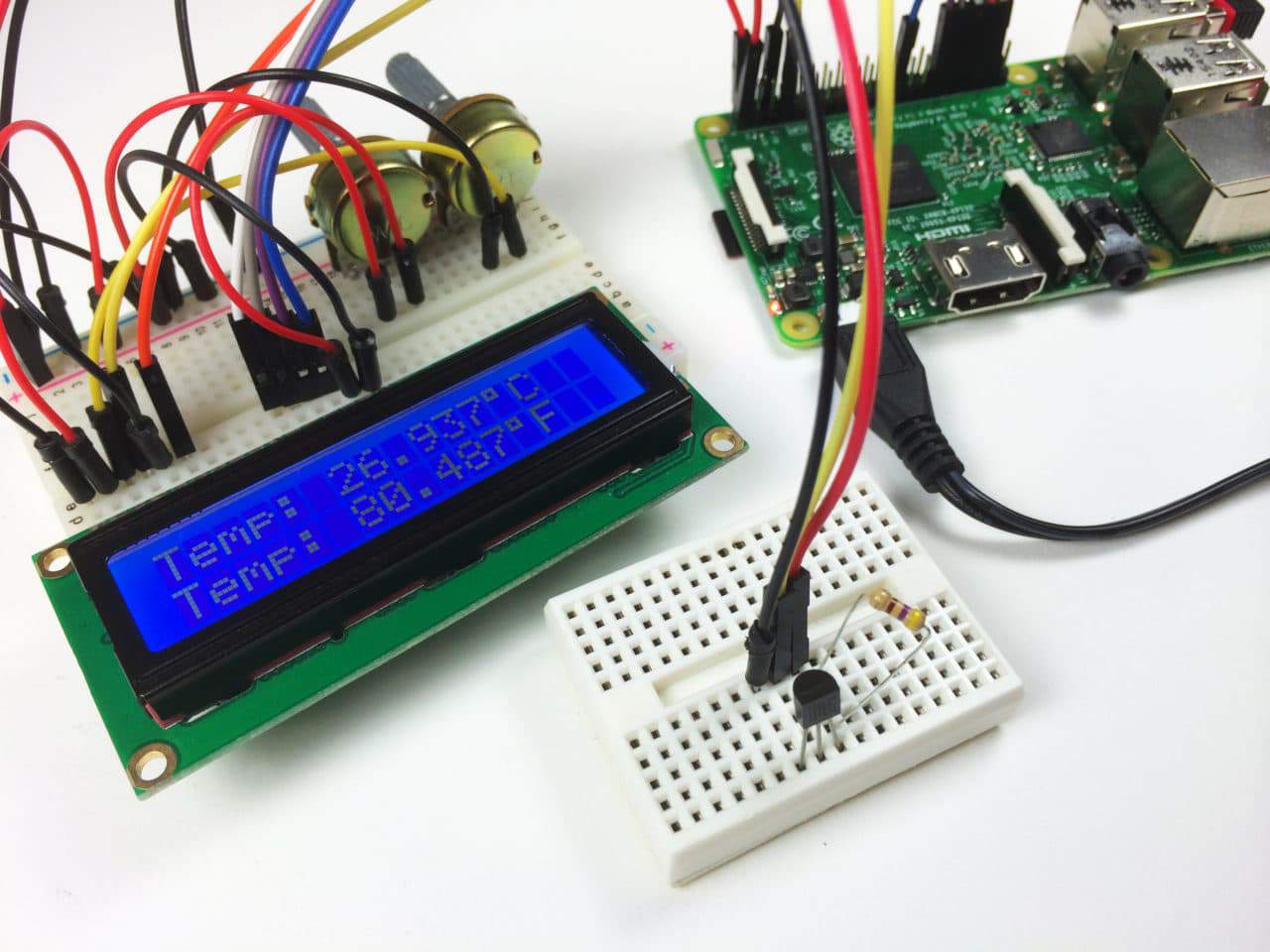
TEMPERATURE OUTPUT TO AN LCD
We’ll be using a Python library called RPLCD to drive the LCD. The RPLCD library can be installed from the Python Package Index, or PIP. PIP might already be installed on your Pi, but if not, enter this at the command prompt to install it:
sudo apt-get install python-pip
After you get PIP installed, install the RPLCD library by entering:
sudo pip install RPLCD
Once you have the library installed, you can run this program to output the temperature to an LCD display:
import os
import glob
import time
from RPLCD import CharLCD
lcd = CharLCD(cols=16, rows=2, pin_rs=37, pin_e=35, pins_data=[33, 31, 29, 23])
os.system('modprobe w1-gpio')
os.system('modprobe w1-therm')
base_dir = '/sys/bus/w1/devices/'
device_folder = glob.glob(base_dir + '28*')[0]
device_file = device_folder + '/w1_slave'
def read_temp_raw():
f = open(device_file, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
return lines
#CELSIUS CALCULATION
def read_temp_c():
lines = read_temp_raw()
while lines[0].strip()[-3:] != 'YES':
time.sleep(0.2)
lines = read_temp_raw()
equals_pos = lines[1].find('t=')
if equals_pos != -1:
temp_string = lines[1][equals_pos+2:]
temp_c = int(temp_string) / 1000.0 # TEMP_STRING IS THE SENSOR OUTPUT, MAKE SURE IT'S AN INTEGER TO DO THE MATH
temp_c = str(round(temp_c, 1)) # ROUND THE RESULT TO 1 PLACE AFTER THE DECIMAL, THEN CONVERT IT TO A STRING
return temp_c
#FAHRENHEIT CALCULATION
def read_temp_f():
lines = read_temp_raw()
while lines[0].strip()[-3:] != 'YES':
time.sleep(0.2)
lines = read_temp_raw()
equals_pos = lines[1].find('t=')
if equals_pos != -1:
temp_string = lines[1][equals_pos+2:]
temp_f = (int(temp_string) / 1000.0) * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32.0 # TEMP_STRING IS THE SENSOR OUTPUT, MAKE SURE IT'S AN INTEGER TO DO THE MATH
temp_f = str(round(temp_f, 1)) # ROUND THE RESULT TO 1 PLACE AFTER THE DECIMAL, THEN CONVERT IT TO A STRING
return temp_f
while True:
lcd.cursor_pos = (0, 0)
lcd.write_string("Temp: " + read_temp_c() + unichr(223) + "C")
lcd.cursor_pos = (1, 0)
lcd.write_string("Temp: " + read_temp_f() + unichr(223) + "F")